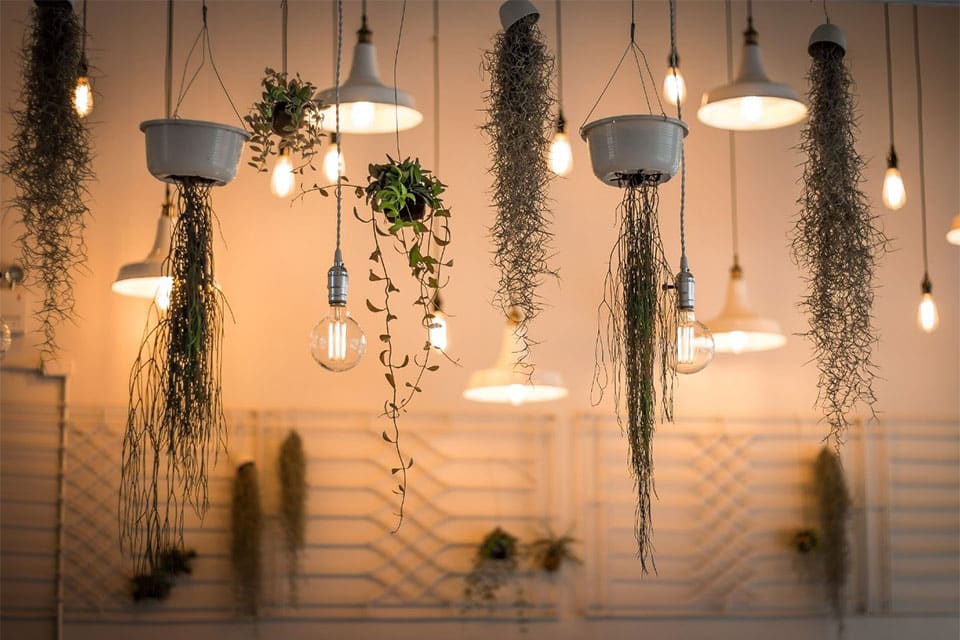
LED filament light bulbs, which are built to look like traditional carbon filament or Edison light bulbs, have captured the attention of many people seeking a unique and stylish look for their exposed bulb pendants and lamps. These replica bulbs offer the same classic look of a traditional filament bulb, but provide greater energy savings.
How exactly do LED filament bulbs manage to recreate the look of an incandescent filament using a light emitting diode, and how does it work? First, we need to look at what exactly LEDs are.
What are LEDs?
Traditional incandescent bulbs create light by generating heat. Unlike other forms of light bulbs that rely on this incandescent heat or a ballast to provide illumination, LEDs have “light emitting diodes” that create only light. This is what makes them so energy-efficient—they’re not wasting energy producing heat in addition to light:
What are Carbon Filament Bulbs?
Incandescent light bulbs have been around for a long time. In standard incandescent bulbs, carbon or tungsten filaments heat up when they are connected to electricity—such as when you flick a light switch—until they are literally “incandescent” with heat and provide light.
In carbon filament or Edison bulbs, these filaments are simply shaped into curly twists, loops, criss-crosses, and lines, and are contained in uniquely shaped glass bulbs such as globe, tubular, pear, and standard:

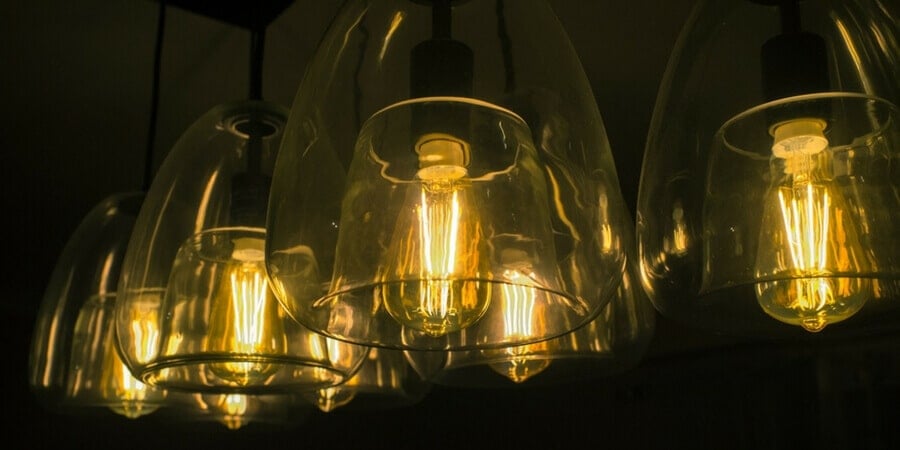
Their elegant appearance and warm light has made them incredibly popular in exposed-bulb lamps, such as pendants.
How do LED filament bulbs work?
Filament LED light bulbs do have an LED “filament”, but instead of heating it up to produce light, this metal strip is actually lined with light emitting diodes (LEDs). The metal strip and LEDs are covered, typically with glass or another transparent material, and then coated with a phosphor to turn the light emitted from the LEDs from blue into—typically—a warmer yellow tone, similar to incandescent filament bulbs. The LEDs strips are positioned facing outwards to reproduce the same 360° angle of light that incandescent bulbs have. When turned on, the entire strip appears illuminated rather than the individual diodes, creating a nice, even glow.

These LED filament strips are available in a number of shades that are designed to emulate the appearance of an incandescent light bulb filament, including many of the same filament patterns. While they are not as thin as the incandescent filament, they look very similar when illuminated.
PRO TIP: LED filament bulbs generate less heat than traditional LEDs (which still emit significantly less heat than incandescent, halogen, or compact fluorescent bulbs) because their diodes are more spaced out. As a result, they dissipate heat more easily and often have even greater longevity than standard LEDs.
4 things to keep in mind when selecting LED filament bulbs
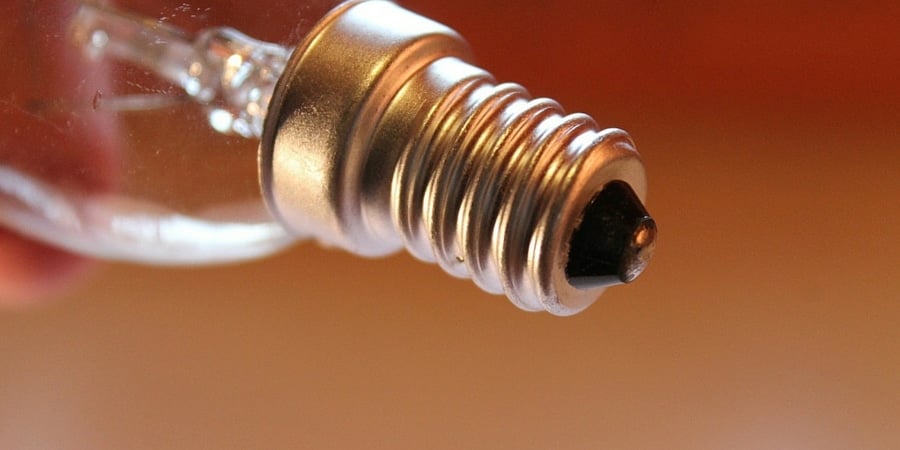
- Light bulb base – It’s important to make sure the light bulb you are selecting will fit in your existing fixture socket. Most LED filament bulbs are available with an Edison screw E27 base or a bayonet cap B22 base, but you can also find smaller fittings such as the small bayonet cap B15 base or the small Edison screw E14 base—sizes commonly used in fixtures such as accent lights and chandeliers.
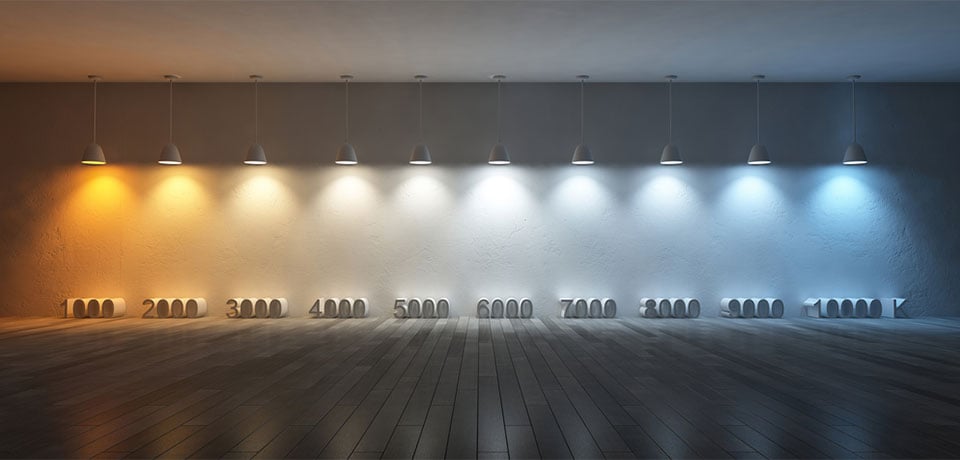
- Correlated Colour Temperature (CCT) – To better emulate incandescent carbon filament lamps, LED filament bulbs are primarily available in warm to very warm whites, though you can find them in other colour temperatures and different hues.
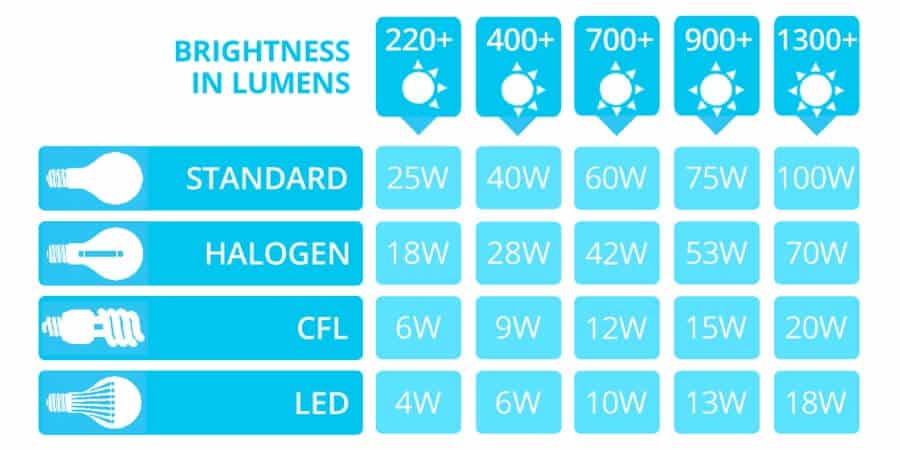
- Brightness – Since filament bulbs are often selected for exposed light fixtures, they are typically not as bright. Check their lumen level rather than their equivalent wattage number to ensure you are getting a bulb with the level of brightness you need.
PRO TIP: Select bulbs with a higher lumen level and invest in a dimmer switch—this way you can easily adjust the lighting to suit any task or situation.
- Dimmer switches – We consider dimmer switches essential to any light fixture. They provide so much more flexibility when it comes to lighting and room ambience, allowing you to adjust the brightness to suit your needs at any given time.
PRO TIP: Some LEDs will work with old dimmer switches, but they are more likely to encounter problems. This is because older switches are typically built using a type of dimming protocol called “mains dimming”, which was designed for the higher wattages required by incandescent light bulbs. Learn more about how to dim LED lights.
When installing dimmer switches, select only LED-compatible options to avoid any buzzing or flickering:
Learn more about what to look for when buying LEDs in our LED buying guide.
Conclusion
LED filaments recreate the look of traditional carbon filament light bulbs by lining up the diodes on a metal strip. This strip is then covered in glass and coated in phosphor to emulate the colour of an incandescent bulb. These metal strips can be shaped into the helices, curls, criss-crosses, and other configurations of carbon filament bulbs, providing you with the same look and ambience of an Edison bulb with all the energy savings of an LED.